

Consequences of "european" settlement
- Menu
- Home
- Haida Gwaii
- Introduced Species
- RGIS
- What did we learn?
- Research
- Publications
- RGIS symposium
- School curriculum
- Contacts
- English
- Français
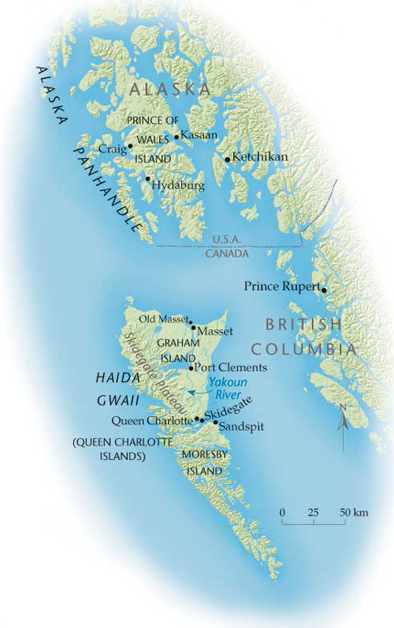
The archipelago |
|||||||||||||
|
Haida
Gwaii
is located on the Northwestern Canadian coast, 80 km off the coasts of |
 |
||||||||||||
| © Canadian Geographic | |||||||||||||
| return to top of page | |||||||||||||
Cultural diversity |
|||||||||||||
|
Haida Gwaii has around 5,000
inhabitants. Over half of them belong to the Haida Nation.
Logging, fishing and tourism are the main industries.
|
 |
||||||||||||
| return to top of page | |||||||||||||
3 main conifers |
|||||||||||||
Old growth
and second growth forest cover most of the islands and are dominated by 3 conifer
tree species:
|
|
||||||||||||
| return to top of page | |||||||||||||
Understory plants diversity |
|||||||||||||
|
Originally
these forests had an understory rich in berry bearing shrubs such as Salal
(Gaultheria shallon), Salmon berry (Rubus spectabilis) or Red Huckleberry
(Vaccinum parviflorum).
|
|||||||||||||
Changes caused by "european" settlement |
|||||||||||||
|
European settlement prompted the development of industrial forest exploitation and the introduction of 143 non-native plant species (22% of the actual plant species found on Haida Gwaii) and of 14 non-native terrestrial mammals (for 11 of them that are indigenous). |
|||||||||||||
| return to top of page | |||||||||||||
|
To know more about the physical setting and the vegetation of Haida Gwaii: |
|||||||||||||



